
Heaters for OEMs in the Plastics Packaging Industry
Enhancing Efficiency and Precision for OEMs with the Best Heaters Used in Plastics Packaging Applications
Consider this your comprehensive guide to heaters used in the plastics packaging industry, where precision meets efficiency to deliver optimal performance in packaging processes. From heat sealers to thermal cutting hot knife cutters, heaters play a crucial role in ensuring consistent temperatures and seamless operations across various packaging applications.
This resource page delves into the key types of heaters utilized in the packaging industry, including cartridge heaters, coil heaters, and nozzle heaters, along with temperature sensors, such as mineral insulated and general-purpose thermocouples. Each heater type offers unique features and benefits tailored to specific packaging applications, ensuring precise temperature control and uniform heat distribution for superior packaging results.
Throughout this pillar page, we'll explore the applications and unique features of each heater type and temperature sensor, highlighting their contributions to enhancing efficiency, precision, and reliability in packaging machinery. Discover how heaters and temperature sensors are revolutionizing the packaging industry and driving advancements in packaging technology.
Read this comprehensive guide in its entirety, or conveniently jump to any section by clicking on the links below.
Market Applications: Selecting the Right Process Heater
Common Issues
Heating Products
Processing Heating
Temperature Sensors
Why Backer Marathon
Market Applications: Selecting the Right Process Heater
Heat Sealers

Heat sealers, also known as heat seal machines or impulse sealers, are used to seal various types of packaging materials, such as plastic bags, pouches, and films, by applying heat to melt the material together. They bond packaging materials together, creating airtight seals that protect products from contamination and spoilage. Heat sealers typically consist of a heating element, a sealing bar or jaw, and a pressure mechanism. Cartridge heaters and coil heaters are commonly employed in heat sealers to provide the precise heat required for sealing various packaging materials.
Here's how they work in a packaging application:
Heating element: The heating element, often made of nichrome wire, generates heat when electricity passes through it. This heating element is usually located within the sealing bar or jaw.
Sealing bar or jaw: The sealing bar or jaw is the part of the heat sealer that presses the packaging material together to create the seal. It is usually made of a heat-resistant material such as aluminum or stainless steel.
Pressure mechanism: The pressure mechanism ensures that the packaging material is firmly pressed together during the sealing process, promoting a tight seal.
When operating the heat sealer, the packaging material is placed between the sealing bar and the base of the machine. The operator then lowers the sealing bar onto the material, activating the heating element. The heat generated by the heating element melts the packaging material, causing it to fuse together. The pressure mechanism ensures that the seal is uniform and secure. Once the sealing process is complete, the sealing bar is lifted, and the sealed package can be removed.
Cartridge heaters are often used in heat sealers to provide the necessary heat for sealing. Cartridge heaters are cylindrical heating elements that consist of a metal sheath enclosing a resistive heating coil. They are inserted into the sealing bar or jaw of the heat sealer and are powered by electricity.
These elements comprise the process by which cartridge heaters work in heat sealers:
Installation: Cartridge heaters are installed into the sealing bar or jaw of the heat sealer, usually by screwing or clamping them into place.
Activation: When the heat sealer is turned on, electricity flows through the cartridge heater, heating up the resistive heating coil inside.
Heat transfer: The heat generated by the cartridge heater is transferred to the sealing bar or jaw, which in turn, heats up the packaging material when it comes into contact with it.
Sealing process: As the packaging material is pressed between the heated sealing bar and the base of the heat sealer, it melts and fuses together, creating a seal.
Control: The temperature of the cartridge heater can usually be controlled by feedback from a thermocouple to ensure that it reaches and stays at the optimal temperature for sealing the specific type of packaging material being used. The thermocouple can either be integral into the heater or separate ly affixed nearby.
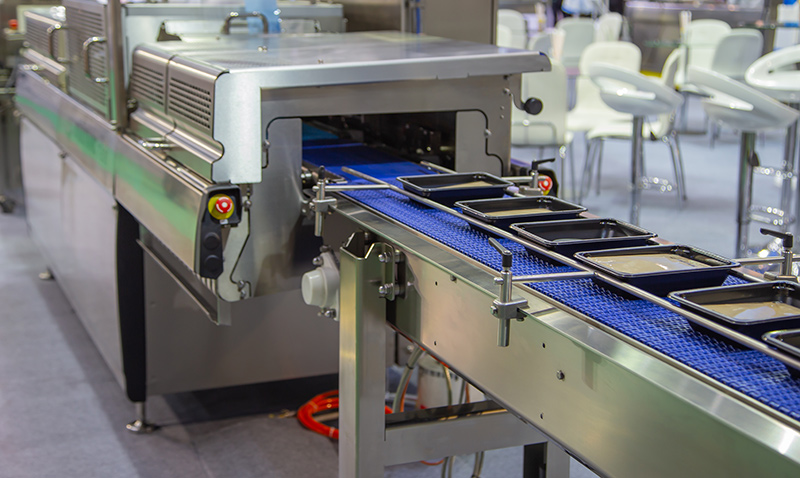

Tray Sealers
Packaging tray sealers are used to seal pre-formed trays or containers typically made of materials like plastic, aluminum, or foam. These sealers are commonly used in the food industry for packaging items such as ready-to-eat meals, fresh produce, and meat products ensuring product freshness and extending shelf life. They work by sealing a film or lid onto the top of the tray to create a secure and tamper-evident package. Cartridge heaters are often employed in packaging tray sealers to provide the necessary heat for the sealing process to create secure seals around the edges of the trays.
Here's how packaging tray sealers work and how they use cartridge heaters:
Tray loading: The trays or containers are loaded onto the sealing machine manually or automatically. These trays are typically pre-formed and may contain food products or other items that need to be packaged.
Film application: A roll of sealing film or pre-cut lids is fed into the sealing machine. The film is positioned over the loaded trays, covering their open tops. In some cases, a vacuum process may be employed to remove air from the trays before sealing.
Sealing station: The sealing station of the machine consists of a heated sealing platen or bar and a corresponding pressure mechanism. The trays with the film covering their tops are moved into position under the sealing platen.
Heat sealing: Cartridge heaters located within the sealing platen heat up when electricity is applied to them. These cartridge heaters are typically positioned evenly throughout the sealing platen to ensure uniform heat distribution. Often, processes will utilize distributed wattage or multi-zone heaters to apply more resistance (heat) to the outer portions of the platen.
Sealing process: When the trays are in position, the sealing platen is lowered onto the trays, bringing the heated surface into contact with the film. The heat from the cartridge heaters melts the film, causing it to bond with the edges of the trays, creating a secure seal. The pressure mechanism ensures that the film is firmly pressed against the trays during the sealing process, promoting a strong seal.
Cooling and release: After the sealing process is complete, the sealing platen is lifted, and the sealed trays are moved to a cooling station where the sealed film solidifies and cools. Once cooled, the trays are released from the machine and can be stacked or further processed for labeling and packaging.
Overall, packaging tray sealers use cartridge heaters in their sealing platens to provide the necessary heat for sealing the film onto pre-formed trays or containers, ensuring the freshness and integrity of the packaged products.

L-Bar Sealers
Packaging L-bar sealers are commonly used for shrink-wrapping products, especially in the packaging of retail goods, food items, and industrial products, providing tamper-evident and protective packaging for retail display. They work by wrapping a film around a product or group of products and then sealing and shrinking the film to create a tight, protective package.
Cartridge heaters play a crucial role in L-bar sealers by providing the consistent heat necessary for sealing the film tightly and securely.
Read below how packaging L-bar sealers work and how they employ cartridge heaters:
Product placement: The product or products to be packaged are placed on a flat surface or conveyor belt within the sealing area of the machine.
Film dispensing: A roll of shrink film is mounted on the machine. The film is unwound from the roll and pulled over the product or products to be packaged. In some cases, the film may be perforated for easier tearing.
L-bar sealing: The L-bar sealing mechanism is brought down over the product and film. The L-bar consists of two perpendicular sealing bars that create a sealed edge along two adjacent sides of the package (forming an "L" shape). These sealing bars are heated by cartridge heaters embedded within them.
Heat sealing: When the L-bar mechanism is lowered, the cartridge heaters within the sealing bars heat up, melting the film at the edges of the package. The heated sealing bars apply pressure to ensure a tight seal. The sealing process is typically activated by a foot pedal or automatic control mechanism.
Trimming: After sealing, excess film outside the sealed edges is trimmed away by a cutting blade or knife, leaving a neatly wrapped package.
Shrink tunnel: The sealed package is then moved into a shrink tunnel, where heat is applied to shrink the film tightly around the product. The heat from the shrink tunnel activates the film's shrink properties, conforming it to the shape of the product and creating a secure package.
Cooling and packaging: Once the film has shrunk and cooled, the packaged product is ready for labeling, storage, or distribution.
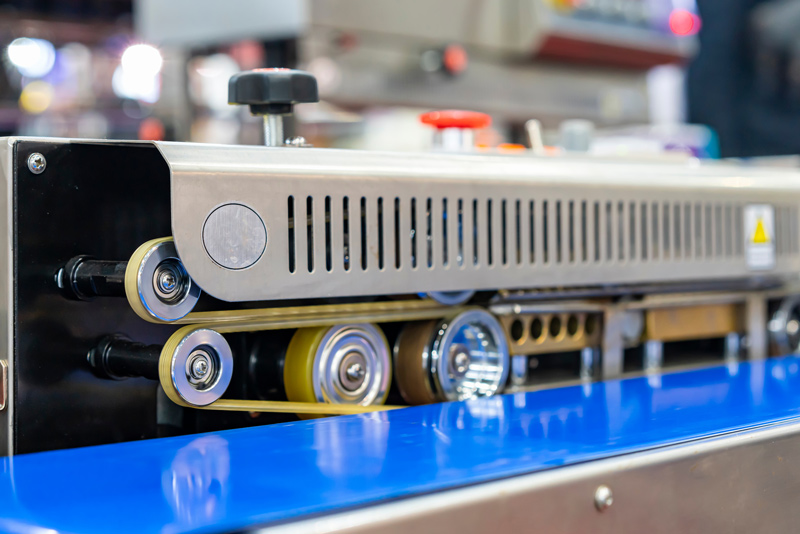
Continuous Band Sealers
Continuous band sealers are commonly used in packaging applications where a continuous sealing process is required, such as sealing bags or pouches filled with various products such as snacks, grains, or powders. These sealers are efficient for high-volume production settings to provide uniform heat sealing along the length of the packaging material. Cartridge heaters are utilized in continuous band sealers to provide the necessary heat for sealing the packaging material.
Below, we describe the process by which continuous band sealers work in packaging and how they use cartridge heaters:
Product loading: The filled bags or pouches are manually or automatically fed into the continuous band sealer. These bags or pouches typically have an open end that needs to be sealed.
Sealing mechanism: The sealing mechanism of the continuous band sealer consists of a heated sealing band or belt and corresponding pressure rollers. The sealing band is typically made of a heat-resistant material and contains embedded cartridge heaters.
Bag transport: The bags or pouches are transported through the continuous band sealer by a conveyor belt system. As they move along the conveyor belt, they pass under the sealing mechanism.
Heat sealing: When a bag or pouch reaches the sealing mechanism, the heated sealing band is lowered onto the open end of the bag. The cartridge heaters embedded within the sealing band heat up, melting the packaging material and creating a seal along the length of the bag. The pressure rollers ensure that the seal is uniform and secure.
Cooling and cutting: After sealing, the sealed bags or pouches continue along the conveyor belt to a cooling station, where the seals solidify and cool. In some continuous band sealers, a cutting mechanism may also be incorporated to separate the sealed bags or pouches from the continuous roll of packaging material.
Packaging discharge: Once cooled and cut, the sealed bags or pouches are discharged from the continuous band sealer, ready for further processing, labeling, or packaging.

Thermal Cutting
Packaging companies utilize thermal cutting methods to precisely cut and seal packaging materials such as plastic films, bags, and pouches. Thermal cutting involves the use of heat to melt and seal the edges of the material, creating a clean and secure seal. Cartridge heaters are often employed in thermal cutting processes to provide the necessary heat for cutting and sealing.
Here's how OEM packaging companies use thermal cutting and how cartridge heaters are used in the process:
Equipment setup: Packaging companies use specialized thermal cutting machines equipped with heating elements and cutting mechanisms. These machines may include heat sealers, bag-making machines, or specialized thermal cutting devices.
Material preparation: The packaging material, typically a plastic film or sheet, is fed into the thermal cutting machine. This material may be in the form of rolls, sheets, or pre-formed bags or pouches.
Heating element activation: Cartridge heaters are installed within the cutting and sealing components of the machine. When the machine is activated, electricity is supplied to the cartridge heaters, causing them to heat up.
Cutting and sealing: As the packaging material passes through the machine, it encounters the heated cutting and sealing elements. The intense heat from the cartridge heaters melts the material along the desired cutting lines, creating a clean, precise cut. Simultaneously, the melted edges are sealed together to prevent fraying and ensure the integrity of the package.
Control and precision: The temperature of the cartridge heaters can be precisely controlled by the use of thermocouples and a controlled loop system to achieve the optimal cutting and sealing conditions for the specific type and thickness of the packaging material being processed. This control ensures consistent results and minimizes the risk of overheating or damage to the material.
Cooling and discharge: After cutting and sealing, the sealed packages or packaging components may pass through a cooling station to solidify and cool the seals. Once cooled, the finished products are discharged from the machine for further processing, labeling, or packaging.
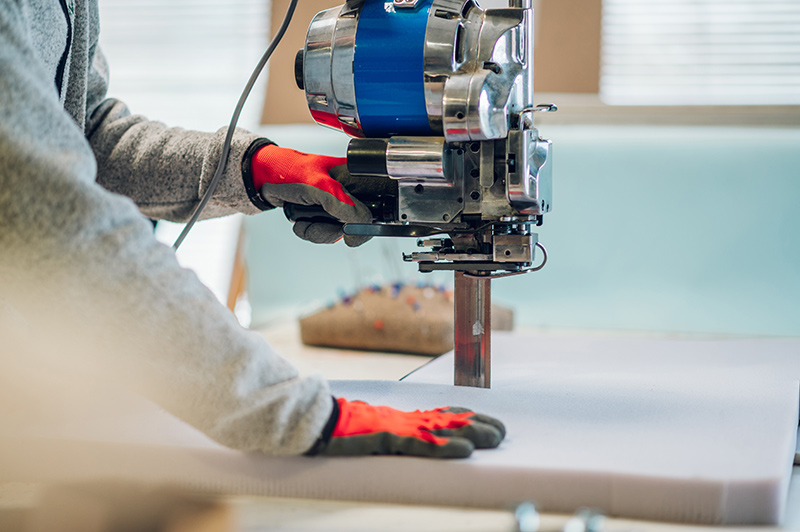

Hot Knife Cutters
Packaging companies utilize hot knife cutter machines to precisely cut through various types of synthetic nylon and polyethylene materials, including plastics, fabrics, and foams. These machines are equipped with a heated blade or knife that melts through the material, resulting in a clean and precise cut. Cartridge heaters are integral components of hot knife cutter machines, providing the heat necessary to heat up the blade to the required temperature for cutting.
We discuss below how packaging companies use hot knife cutter machines and how cartridge heaters are used in the process:
Machine set-up: The hot knife cutter machine consists of a cutting platform, a heated blade or knife, and a control system. Cartridge heaters are installed within the blade or knife assembly.
Material preparation: The material to be cut is placed on the cutting platform of the machine. This material can vary widely and may include plastic films, foam sheets, textile fabrics, or other similar materials.
Heating element activation: Cartridge heaters, embedded within the blade or knife assembly, are activated by supplying electricity to them. As the cartridge heaters heat up, they transfer heat to the blade, causing it to reach the desired cutting temperature.
Cutting operation: Once the blade reaches the appropriate temperature, the operator initiates the cutting process. The heated blade is brought into contact with the material to be cut. The intense heat from the blade melts through the material, creating a clean and precise cut along the desired path.
Control and precision: The temperature of the cartridge heaters can be precisely controlled to achieve the optimal cutting conditions for the specific type and thickness of the material being processed. This control ensures consistent cutting results and minimizes the risk of overheating or damage to the material.
Cooling and discharge: After cutting, the material may pass through a cooling station to allow the cut edges to solidify and cool. Once cooled, the cut pieces are discharged from the machine for further processing or packaging.

Thermal Forming
In packaging, thermal forming is a process used to shape thermoplastic materials, such as plastic sheets, into desired shapes, such as trays, containers, or blister packs, by heating the material until it becomes pliable and then forming it over a mold or template. Cartridge heaters play a crucial role in thermal forming processes by providing the necessary heat to soften the thermoplastic material and facilitate accurate and uniform shaping of packaging materials.
Thermal forming utilizes cartridge heaters in the packaging industry in the following way:
Heating stage: The thermoplastic material, typically in the form of sheets or rolls, is fed into a thermal forming machine. Cartridge heaters are positioned within the heating elements of the machine. When the machine is activated, electricity is supplied to the cartridge heaters, causing them to heat up.
Heating the material: The thermoplastic material passes through the heating zone of the thermal forming machine, where it is subjected to controlled heat from the cartridge heaters. The heat softens the material, making it pliable and flexible for shaping.
Forming stage: Once the material reaches the desired temperature, it is transferred to the forming station of the machine. Here, the softened material is pressed over a mold or template using pneumatic or mechanical pressure. The mold or template defines the shape of the final packaging product.
Cooling stage: After forming, the shaped material is cooled using air or water to solidify it into the desired shape. This cooling process may occur within the thermal forming machine or in a separate cooling station.
Trimming and finishing: Once cooled, the formed packaging products may undergo additional trimming or finishing processes to remove any excess material and refine the final shape.
Common Issues
Common issues in these areas can include vibration or flexing, moisture applications, and mechanical strength, among others. As an example, in instances where motion (up and down/open and close), is a factor, Backer Marathon can supply Epoxylite® or Teflon® seals along with Teflon® or silicon lead wires to extend the life of the heater. The charts below provide more information about what adjustments can be made for you in varying circumstances. These possibilities—along with our 9-day lead time, unique in the industry—give you very valuable, dependable options.
| Cement | Provides protection against some thicker liquids and dust, however it is not waterproof. It is also somewhat brittle and subject to cracking in high impact or high vibration applications. Up to 2600°F. |
| Ceramic | A steatite endpiece provides excellent strength and temperature resistance. However it offers little protection against moisture or other contaminats. |
| Lava Seal | A swaged in lava plug protects the internal cartridge from contamination. Up to 1500°F. |
| Teflon® Seal |
|
| Epoxy Potting | Provides a very good seal with excellent mechanical strength. However, it's adherence to Teflon or silicone rubber lead wire is only fair. It is rated up to 265°F and bonds well to Duraflex lead wire. |
| Epoxylite Potting | Provides similar mechanical properties as epoxy potting. Up to 600°F. |
| RTV |
|
Chart
| End Seal Type | Max Temp | Moisture Protection | Contamination | Mechanical Strength | Vibration Resistance | Moisture Applications | Vibration or Flexing | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Cement Potting | 2600°F | Poor | Fair | Good | Poor | Poor | Poor |
 |
Ceramic End Piece | 2500°F | Poor | Poor | Excellent | Excellent | Poor | Good |
 |
Mica Seal | 2500°F | Poor | Good | Average | Average | Poor | Fair |
 |
Lava Seal | 1500°F | Poor | Good | Fair | Poor | Poor | Poor |
.jpg) |
Epoxylite Potting | 600°F | Good | Very Good | Very Good | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
.jpg) |
RTV w/ Silicone Rubber Leads | 392°F | Excellent | Excellent | Fair | Good | Excellent | Average |
 |
Teflon® Seal | 350°F | Good | Excellent | Very Good | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
.jpg) |
Epoxy Potting | 265°F | Good | Good | Excellent | Excellent | Good | Good |
Heating Products
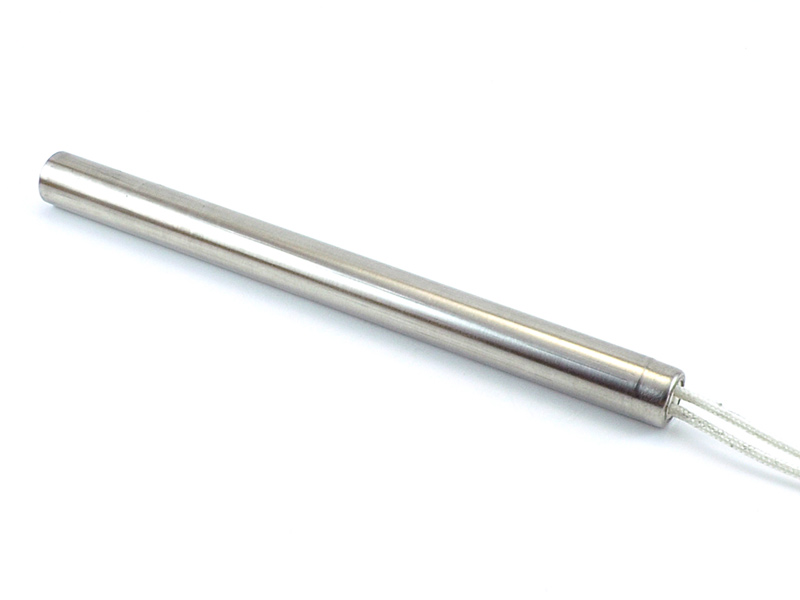

Cartridge Heaters
Renowned for their versatility and efficiency, cartridge heaters are widely used in packaging machinery for their ability to deliver high heat output in a compact and durable design. These heaters are ideal for applications such as heat sealers, tray sealers, and L-bar sealers, where precise temperature control is essential for achieving strong and reliable seals.
Backer Marathon is a leading manufacturer of American-made high-watt density cartridge heaters. Our HotRod stainless steel heaters are the industry standard and offer quality construction, superior heat transfer, and long-life heating solutions up to 1600°F. In addition to our swaged heaters, we offer non-swaged heaters for applications up to 800°F, as well as square heaters for milled slot solutions.
Choose from one of our thousands of in stock models or let our engineers design a custom heater for your application. If you have questions about OEM cartridge or replacement cartridge heaters, please Contact Us or call (830) 775-1417. Nosotros hablamos español.
Click Here for More Information on Cartridge Heaters for OEM Requirements.
Coil Heaters
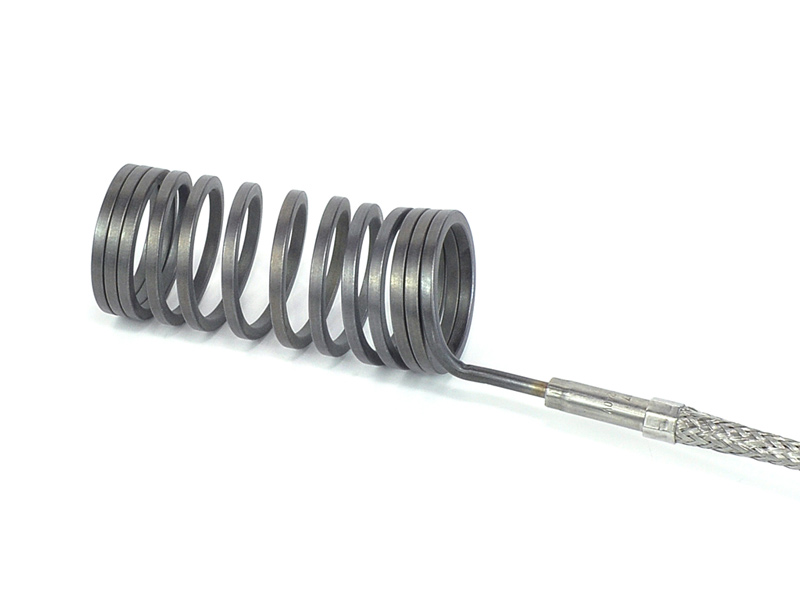

Coil heaters are characterized by their flexibility and fast heat-up times, making them well-suited for applications requiring rapid heating and precise temperature uniformity. They are commonly employed in continuous band sealers, where consistent heat sealing along the length of the packaging material is critical for maintaining product integrity and freshness.
When highly focused heat is required, and a very low profile is imperative, coil heaters are the best cost-effective option. Coil heaters may be used to concentrate the heat on specific segments, or the coil may be spread to equalize the temperature across the object to be heated. Backer Marathon stocks a wide variety of coil heaters, OEM replacement heaters, and will provide custom configurations upon request.
Click Here for More Information on Coil Heaters for OEM Requirements.

Nozzle Heaters
Nozzle heaters are specifically designed to fit snugly around injection molding nozzles, providing efficient heating for thermal forming processes in the packaging industry. With their compact and durable construction, these heaters ensure uniform heat distribution, enabling precise molding and shaping of packaging materials for optimal packaging performance.
Backer Marathon nozzle heaters feature a range of attributes, including an oxidation-resistant metal sheath that ensures durability, protective sleeving at lead exits for added safety measures, and a stainless steel clamping strap with secure barrel nuts and screws. Available in diameters ranging from 1" to 3" and widths from 1" to 6", the heater also offers versatility. It can be constructed in a low-profile wedgelock design and boasts a high-temperature oxidation-resistant sheath, top-grade mica insulation for excellent electrical insulation even in humid conditions, and a nickel/chromium resistance wire wound uniformly for consistent heat distribution. Additionally, the clamping band is made of low thermal expansion stainless steel for reliable clamping pressure at high temperatures, while the standard 10" fiberglass leadwires, rated up to 850 degrees F, provide protection.
Click Here for More Information on Nozzle Heaters for OEM Requirements.
Sensors
-(1).jpg)
Temperature Sensors
Backer Marathon provides a line of premium temperature sensors. We offer standard thermocouples, mineral insulated thermocouples, and RTDs. We carry hundreds of different models in stock and offer quick turnaround, usually 48 hours or less, on custom-designed and manufactured units. We use only the highest-grade materials and offer a variety of sheath materials for any environment or temperature range. All sensors are subject to rigid quality control procedures and a thorough inspection process. Expert engineering assistance is readily available for any order size, large or small. In addition to your sensor needs, Backer Marathon can engineer a complete thermal system for you.
Click Here for More Information on Thermocouples for OEM Requirements.
.jpg)
Mineral Insulated Sensors
Known for their ruggedness and accuracy, mineral insulated thermocouples are commonly used in packaging machinery to monitor and regulate temperatures during the sealing and cutting processes. These sensors offer reliable temperature measurement in high-temperature environments, ensuring consistent and repeatable packaging results.
Click Here for More Information on Mineral Insulated Thermocouples for OEM Requirements.
1.jpg)
General-Purpose Sensors
General-purpose thermocouples provide cost-effective temperature monitoring solutions for a wide range of packaging applications. Whether used for temperature control in heat sealers or thermal cutting hot knife cutters, these sensors offer versatility and reliability, making them essential components in packaging machinery.
The selection of industrial heaters depends on factors such as your specific plastic packaging application, required temperatures, and the size and configuration of the processing equipment. Each type of heater serves a unique purpose in contributing to the efficient and controlled processing of plastics in the packaging industry.
Click Here for More Information on General-Purpose Thermocouples for OEM Requirements.
Why Backer Marathon
Our loyal customers have come to know that we anticipate their needs because we actively search for solutions. This is reflected in our advanced quality planning (AQP) lens focused on all that we do. It allows us to be nimble, congruent, and efficient with processes and production. We and our customers benefit from this lean, lessons-learned perspective for each new—or existing—project we successfully execute.
Backer Marathon is part of the Backer North America Group, serving OEMs globally. Being linked with our sister companies under this umbrella provides a wide breadth and depth of resources, expertise, and experience that OEMs benefit from. We collaborate fully with our colleagues, and will source—and manage—the stock and unique custom-heating solutions you need.
We believe in hard work, creative engineering, and excellent customer service. Whether you need one piece or one thousand, Backer Marathon is committed to providing you with exactly what you need when you need it. As we innovate and lead the industry with unparalleled engineering and customer service, we look forward to helping you continue to grow with us.
Let's talk about your next project. Contact us now or call us today at 1 (830) 775-1417. Nosotros hablamos español. We're excited to collaborate with you.









